AI Arena - 0xepley's results
In AI Arena you train an AI character to battle in a platform fighting game. Imagine a cross between Pokémon and Super Smash Bros, but the characters are AIs, and you can train them to learn almost any skill in preparation for battle.
General Information
Platform: Code4rena
Start Date: 09/02/2024
Pot Size: $60,500 USDC
Total HM: 17
Participants: 283
Period: 12 days
Judge:
Id: 328
League: ETH
Findings Distribution
Researcher Performance
Rank: 40/283
Findings: 1
Award: $166.17
🌟 Selected for report: 0
🚀 Solo Findings: 0
Findings Information
🌟 Selected for report: 0xSmartContract
Also found by: 0xAsen, 0xDetermination, 0xStriker, 0xblack_bird, 0xbrett8571, 0xepley, 0xweb3boy, 14si2o_Flint, Bauchibred, DarkTower, JayShreeRAM, JcFichtner, K42, McToady, Myd, PoeAudits, Rolezn, SAQ, ZanyBonzy, aariiif, albahaca, ansa-zanjbeel, cheatc0d3, clara, cudo, dimulski, fouzantanveer, foxb868, hassanshakeel13, hunter_w3b, kaveyjoe, klau5, peanuts, pipidu83, popeye, rspadi, scokaf, shaflow2, tala7985, wahedtalash77, yongskiws
Awards
166.1676 USDC - $166.17
Labels
External Links
🛠️ AI Arena
In AI Arena you train an AI character to battle in a platform fighting game. Imagine a cross between Pokémon and Super Smash Bros, but the characters are AIs, and you can train them to learn almost any skill in preparation for battle.
Summary
| List | Head | Details |
|---|---|---|
| a) | Overview of the AI Arena Project | Summary of the whole Protocol |
| b) | Technical Architecture | Architecture of the smart contracts |
| c) | The approach I would follow when reviewing the code | Stages in my code review and analysis |
| d) | Analysis of the code base | What is unique? How are the existing patterns used? "Solidity-metrics" was used |
| e) | Test analysis | Test scope of the project and quality of tests |
| f) | Security Approach of the Project | Audit approach of the Project |
| g) | In-depth architecture assessment of business logic | Architecture of the Protocol |
| h) | Codebase Quality | Overall Code Quality of the Project |
| i) | Other Audit Reports and Automated Findings | What are the previous Audit reports and their analysis |
| j) | Contract Functionalities | Functionality of different Contracts involved |
| k) | Full representation of the project’s risk model | What are the risks associated with the project |
| l) | Packages and Dependencies Analysis | Details about the project Packages |
| m) | New insights and learning of project from this audit | Things learned from the project |
| n) | Point of improvements | Things that could be improved |
a) Overview of the AI Arena Project
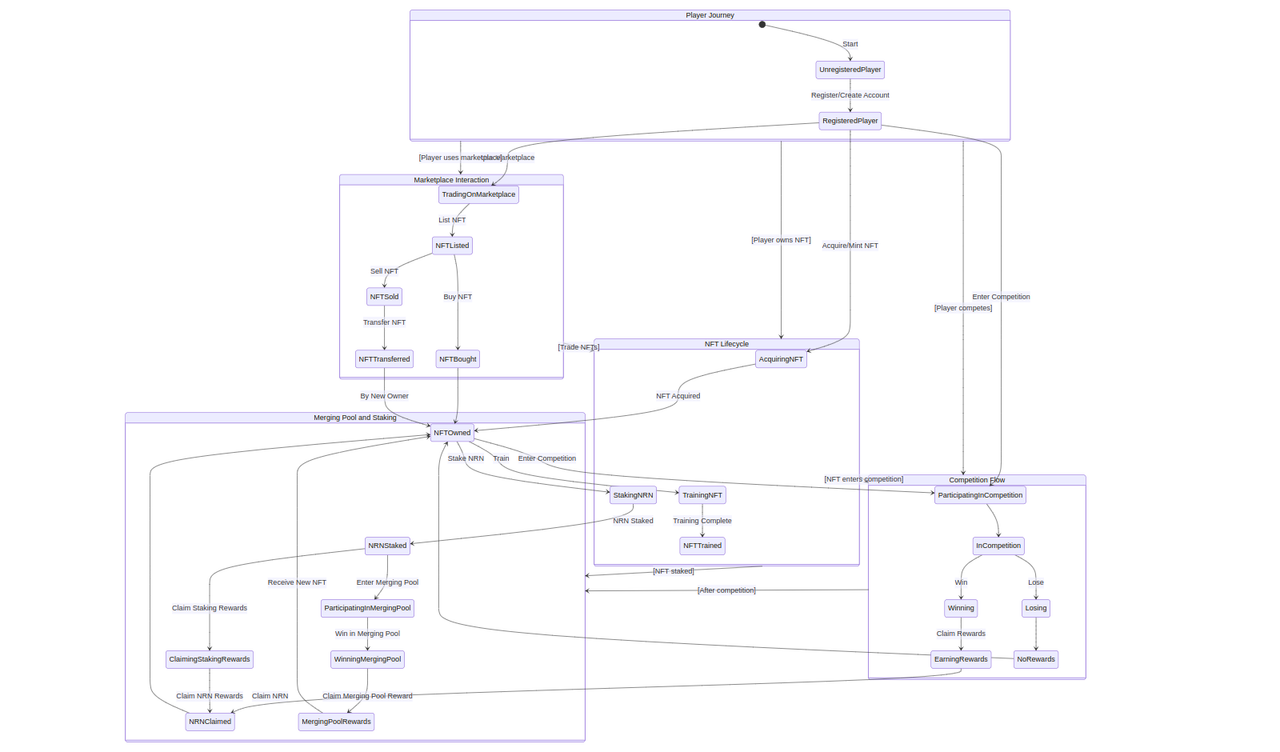
The AI Arena is a comprehensive blockchain-based ecosystem that integrates NFT (Non-Fungible Token) technology with competitive gaming and an innovative economic model. This ecosystem allows users to own, train, and compete with unique digital fighters represented as NFTs, engaging in ranked battles within a global competitive landscape. Central to its economy is the Neuron ($NRN) token, which facilitates transactions, staking, and rewards within the AI Arena.
Key Components of the AI Arena:
-
NFT Fighters: Players can acquire unique digital fighters as NFTs, each with distinct attributes and abilities. These fighters are central to the gameplay, as players train them to improve their stats and battle other players' fighters in the arena.
-
Gaming Competitions: AI Arena hosts ranked battles where players can enter their NFT fighters to compete against others. Success in these battles improves the player's and the fighter's global rankings, unlocking potential rewards and recognition within the community.
-
Economic Model and $NRN Token: The ecosystem is powered by the Neuron ($NRN) token, an in-game currency that players can earn, stake, and spend within the AI Arena. It is used for various purposes, including entering competitions, staking on outcomes, purchasing in-game items, and accessing special features or events.
-
Staking and Rewards: Players have the opportunity to stake $NRN tokens on their fighters or outcomes of battles, incentivizing active participation and investment in the game's economy. Staking mechanisms are designed to reward skill, strategy, and engagement, distributing $NRN tokens as rewards based on performance in competitions and other criteria.
-
Merging Pool: A unique feature of the AI Arena is the merging pool, where players can potentially upgrade their fighters by combining them with others. This process involves staking NFTs and $NRN tokens, offering a chance to obtain fighters with enhanced attributes and rarity.
b) Technical Architecture:
<br/>AI Arena architecture is built around a set of smart contracts, each serving specific roles:
Given the detailed examination of the AI Arena project's smart contracts, here is a summary that outlines the core functionalities, technical characteristics, and their importance and management within the protocol:
<br/>| File Name | Core Functionality | Technical Characteristics | Importance and Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| AiArenaHelper.sol | Manages AI Arena fighters' attributes. | Implements probabilistic attribute assignment based on fighter DNA. Uses mappings for attribute probabilities. | Critical for fighter diversity and gameplay dynamics. Managed through attribute adjustments and generation updates. |
| FighterFarm.sol | Main contract for NFT fighter creation, ownership, and trading. | ERC721 implementation with extended functionalities for NFT locking, minting, and burning. Interacts with AiArenaHelper for attribute generation. | Central to user interaction with NFT fighters. Requires secure management of NFT minting and trading. |
| FighterOps.sol | Provides utility functions for managing Fighter NFTs. | Library used for structuring fighter data and emitting creation events. Simplifies fighter information handling. | Essential for efficient fighter data management and interaction within other contracts. |
| GameItems.sol | Manages in-game items and resources. | ERC1155 multi-token standard for diverse in-game items. Supports minting, burning, and trading of items with finite supply management. | Key for adding depth to the game economy and player strategy. Managed via admin controls for item properties. |
| MergingPool.sol | Facilitates the merging of fighters for upgrades. | Allows users to stake fighters and NRNs to participate in merging, aiming to win upgraded fighters. Implements winner selection based on points. | Integral to game progression and NFT value enhancement. Requires careful balance of reward mechanisms. |
| Neuron.sol | Manages the Neuron (NRN) token economy. | ERC20 token with roles for minting and burning. Supports airdrops and token claims. | Foundation of the in-game economy. Management involves controlling token supply and distribution. |
| RankedBattle.sol | Core gameplay contract for ranked battles and staking. | Manages battle entries, outcomes, and rewards. Interacts with VoltageManager for fight mechanics. | Central to player engagement and competitive gameplay. Requires secure and fair implementation of battle logic. |
| StakeAtRisk.sol | Manages at-risk stakes during competition rounds. | Keeps track of NRNs at risk due to battle losses. Allows for stake reclamation or loss. | Important for adding risk elements to staking. Managed to ensure fair risk-reward balance for players. |
| VoltageManager.sol | Manages voltage, a resource for initiating battles. | Controls voltage replenishment and spending. Integrates with GameItems for battery usage. | Crucial for regulating battle participation and pacing. Management involves balancing resource availability. |
Explanation
AiArenaHelper.sol This contract is responsible for generating and managing the physical attributes of AI Arena fighters. It utilizes a probabilistic approach to assign attributes based on the fighter's DNA, allowing for a diverse range of fighters with unique characteristics. This variability plays a crucial role in the game dynamics and fighter development.
FighterFarm.sol This is the primary contract for creating, owning, and trading NFT fighters within the AI Arena. It extends the ERC721 standard to include functionalities such as locking (preventing trades under certain conditions), minting new fighters, and burning fighters. It interacts with the AiArenaHelper to determine fighters' attributes, making it central to user engagement with the game's NFT assets.
FighterOps.sol FighterOps is a library that provides utility functions for managing Fighter NFTs. It structures fighter data, making it easier to handle within other contracts, and emits events upon the creation of new fighters. This library ensures efficient and standardized management of fighter information across the ecosystem.
GameItems.sol This contract manages the various in-game items and resources available within AI Arena, utilizing the ERC1155 standard for a multi-token approach. It supports the minting, burning, and trading of items, some of which may have a finite supply. The contract adds depth to the game's economy and player strategies through the diverse utility of items.
MergingPool.sol The MergingPool facilitates the process of merging fighters to potentially create upgraded versions. Players can stake their fighters and NRN tokens in hopes of winning a more powerful fighter based on points accumulated in the pool. This contract is integral to game progression and enhancing the value of NFTs within the ecosystem.
Neuron.sol Neuron.sol manages the Neuron (NRN) token, the primary currency within AI Arena's economy. It's an ERC20 token contract with functionalities for minting, burning, airdropping, and claiming tokens. This contract underpins the entire in-game economy, dictating transactions, rewards, and staking mechanisms.
RankedBattle.sol RankedBattle is at the core of AI Arena's gameplay, managing ranked battles, staking NRNs on fighters, and distributing rewards based on battle outcomes. It coordinates with the VoltageManager to regulate fight entries and ensures a competitive and engaging environment for players.
StakeAtRisk.sol This contract manages the stakes that are at risk during competition rounds. When players lose battles under certain conditions, a portion of their staked NRNs becomes at risk of being lost. This mechanism introduces a risk-reward dynamic to staking, adding a layer of strategy to participating in ranked battles.
VoltageManager.sol VoltageManager oversees the voltage system, a key resource required for initiating battles in AI Arena. It manages voltage replenishment and expenditure, integrating with GameItems for additional functionalities like using batteries to recharge voltage. This contract is crucial for maintaining an active and balanced competitive scene within the game.
<br/>State Model of the Protocol
<br/>c) The approach I would follow when reviewing the code
First, by examining the scope of the code, I determined my code review and analysis strategy. https://code4rena.com/audits/2024-02-ai-arena#top
Accordingly, I would analyze and audit the subject in the following steps;
| Number | Stage | Details | Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Compile and Run Test | Installation | Test and installation structure is simple, cleanly designed |
| 2 | Architecture Review | Al Arena | Provides a basic architectural teaching for General Architecture |
| 3 | Test Suits | Tests | In this section, the scope and content of the tests of the project are analyzed. |
| 4 | Manual Code Review | Scope | |
| 5 | Using Solodit for common vulnerabilities | Solodit | Using solodit to find common vulnerabilites related to NFT protocol |
| 6 | Infographic | Figma | Tried to make Visual drawings to understand the hard-to-understand mechanisms |
| 7 | Special focus on Areas of Concern | Areas of Concern | Code where I should focus more |
d) Analysis of the code base
The most important summary in analyzing the code base is the stacking of codes to be analyzed. In this way, many predictions can be made, including the difficulty levels of the contracts, which one is more important for the auditor, the features they contain that are important for security (payable functions, uses assembly, etc.), the audit cost of the project, and the time to be allocated to the audit; Uses Consensys Solidity Metrics
-
filename: This field indicates the language in which smart contracts are written
-
Language: Language in which the codebase is written.
-
Code: This field indicates the number of actual lines of code in the smart contract.
-
Comment: This field indicates the number of lines in the smart contract.
-
Blank: This field indicates the number of Blank lines in the smart contract.
-
Total: This field indicates the number of Total lines (code + comment + blank) in the smart contract.
Analysis of sloc of core contracts
Total : 9 files, 1283 codes, 766 comments, 328 blanks, all 2377 lines
Files
| filename | language | code | comment | blank | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| src/AiArenaHelper.sol | Solidity | 107 | 53 | 28 | 188 |
| src/FighterFarm.sol | Solidity | 327 | 159 | 61 | 547 |
| src/FighterOps.sol | Solidity | 74 | 21 | 10 | 105 |
| src/GameItems.sol | Solidity | 163 | 109 | 44 | 316 |
| src/MergingPool.sol | Solidity | 110 | 72 | 30 | 212 |
| src/Neuron.sol | Solidity | 92 | 81 | 34 | 207 |
| src/RankedBattle.sol | Solidity | 300 | 161 | 74 | 535 |
| src/StakeAtRisk.sol | Solidity | 63 | 58 | 24 | 145 |
| src/VoltageManager.sol | Solidity | 47 | 52 | 23 | 122 |
Dependencies / External Imports
@openzeppelin/contracts/access/AccessControl.sol@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC1155/ERC1155.sol@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721Enumerable.sol
Comment-to-Source Ratio:
On average there are 1.66 code lines per comment (lower=better).
e) Test analysis
Setup
Clone with recurse:
git clone --recurse https://github.com/code-423n4/2024-02-ai-arena.git
Install libraries using forge and compile contracts.
forge install forge build
After installing and building contracts I ran this command to execute all the test scripts:
forge test
To execute an indivial test I did it using
forge test --match-path test/AiArenaHelper.t.sol -vvvv
To print the gas report of contracts I simply ran:
forge test --gas-report
See code coverage by running this command:
forge coverage --ir-minimum
What did the project do differently? ;
-
- It can be said that the developers of the project did a quality job, there is a test structure consisting of tests with quality content. In particular, tests have been written successfully.
-
- Overall line coverage percentage provided by your tests : 90%
What could they have done better?
-
- If we look at the test scope and content of the project with a systematic checklist, we can see which parts are good and which areas have room for improvement As a result of my analysis, those marked in green are the ones that the project has fully achieved. The remaining areas are the development areas of the project in terms of testing ;
Ref:https://xin-xia.github.io/publication/icse194.pdf
- 2): It is recommended to increase the test coverage to 100% so make sure that each and every line is battle tested
f) Security Approach of the Project
Successful current security understanding of the project;
1- The project hasn't underwent any audit(nothing stated in the docs), this innovative assessments on Code4rena is the first one, where multiple auditors are scrutinizing the code.
What the project should add in the understanding of Security;
1- By distributing the project to testnets, ensuring that the audits are carried out in onchain audit. (This will increase coverage)
2- Add On-Chain Monitoring System; If On-Chain Monitoring systems such as Forta are added to the project, its security will increase.
For example ; This bot tracks any DEFI transactions in which wrapping, unwrapping, swapping, depositing, or withdrawals occur over a threshold amount. If transactions occur with unusually high token amounts, the bot sends out an alert. https://app.forta.network/bot/0x7f9afc392329ed5a473bcf304565adf9c2588ba4bc060f7d215519005b8303e3
3- After the Code4rena audit is completed and the project is live, I recommend the audit process to continue, projects like immunefi do this. https://immunefi.com/
4- Emergency Action Plan In a high-level security approach, there should be a crisis handbook like the one below and the strategic members of the project should be trained on this subject and drills should be carried out. Naturally, this information and road plan will not be available to the public. https://docs.google.com/document/u/0/d/1DaAiuGFkMEMMiIuvqhePL5aDFGHJ9Ya6D04rdaldqC0/mobilebasic#h.27dmpkyp2k1z
5- I also recommend that you have an "Economic Audit" for projects based on such complex mathematics and economic models. An example Economic Audit is provided in the link below; Economic Audit with Three Sigma
6 - As the project team, you can consider applying the multi-stage audit model.
Read more about the MPA model; https://mpa.solodit.xyz/
7 - I recommend having a masterplan applied to project team members (This information is not included in the documents). All authorizations, including NPM passwords and authorizations, should be reserved only for current employees. I also recommend that a definitive security constitution project be found for employees to protect these passwords with rules such as 2FA. The LEDGER hack, which has made a big impact recently, is the best example in this regard;
https://twitter.com/Ledger/status/1735326240658100414?t=UAuzoir9uliXplerqP-Ing&s=19
g) In-depth architecture assessment of business logic
The AI Arena's architecture is designed around a core principle of integrating blockchain technology with competitive AI gaming. This results in a multi-faceted ecosystem that leverages NFTs, a proprietary utility token (NRN), and smart contracts to create a dynamic and engaging user experience. The protocol's business logic is embedded within its smart contracts, ensuring transparency, security, and fairness for all participants. Here's an in-depth assessment of its architecture and business logic:
-
NFT Fighters and Ownership: Central to AI Arena are NFT Fighters, each uniquely represented on the blockchain, providing verifiable ownership and scarcity. These NFTs are not just collectibles but are integral to the gameplay, acting as the avatars through which players interact with the AI Arena ecosystem. The Fighters' attributes and training progress are stored immutably, ensuring that each NFT evolves in a way that is transparent and tamper-proof.
-
Neuron (NRN) Token Economy: The NRN token is the lifeblood of the AI Arena, facilitating transactions, staking, and governance within the ecosystem. It's used for purchasing NFT Fighters, entering competitions, staking on outcomes, and claiming rewards. This creates a circular economy where tokens are recycled through various aspects of the game, driving engagement and incentivizing participation.
-
Gaming Competitions and Leaderboard: The protocol hosts AI-driven competitions where NFT Fighters battle based on their training and attributes. Success in these competitions is rewarded with NRN tokens and higher leaderboard rankings, fostering a competitive environment. The leaderboard is a smart contract that dynamically updates based on competition outcomes, ensuring real-time tracking of players' standings.
-
Staking and Rewards Mechanism: Players can stake NRN tokens on their Fighters or competition outcomes, integrating a DeFi element into the gaming experience. The staking mechanism is designed to reward players for active participation and successful predictions, distributing rewards from a pool accumulated through entry fees and other in-game activities. This mechanism is carefully balanced to ensure sustainability and to incentivize long-term engagement.
-
Merging Pool and Fighter Evolution: The merging pool offers a unique feature where players can stake their NFT Fighters to gain access to upgrades or new Fighters, enhancing their capabilities. This introduces an element of strategy and resource management, as players must decide the best way to allocate their assets for optimal growth and performance.
Architectural Interactions
The interaction between the NFT and ERC20 contracts forms the backbone of the project's business logic. Assets are tokenized into NFTs, each with its revenue-generation capabilities. The revenue is then pooled and distributed through the ERC20 tokens, linking the asset management component directly with investor returns. This architecture facilitates a direct correlation between the performance of individual assets and the dividends received by investors, embedding transparency and fairness into the business model.
The allowlist mechanism further interacts with the ERC20 token distribution process, ensuring that only eligible participants receive revenue. This interaction underscores the project's commitment to regulatory compliance and security, integrating these considerations seamlessly into the business logic.
h) Codebase Quality
Overall, I consider the quality of the AI Arena protocol codebase to be Good. The code appears to be mature and well-developed. We have noticed the implementation of various standards adhere to appropriately. Details are explained below:
| Codebase Quality Categories | Comments |
|---|---|
| Architecture & Design | The protocol features a modular design, segregating functionality into distinct contracts (e.g., FighterFarm, RankedBattle, MergingPool) for clarity and ease of maintenance. The use of libraries like FixedPointMathLib for mathematical operations also indicates thoughtful design choices aimed at optimizing contract performance and gas efficiency. |
| Security Practices | The contracts demonstrate awareness of common security pitfalls in Solidity development. Functions are guarded with appropriate access control modifiers (e.g., onlyOwner, isAdmin checks), and state-changing functions are protected against reentrancy attacks. However, a comprehensive external security audit would be necessary to validate the absence of deeper vulnerabilities. |
| Upgradeability & Flexibility | The project does not explicitly implement upgradeability patterns (e.g., proxy contracts), which might impact long-term maintainability. Considering an upgrade path or versioning strategy could enhance the project's flexibility in addressing future requirements.. |
| Efficiency & Gas Optimization | The code demonstrates an awareness of gas optimization in some areas, such as using mappings for efficient data storage. However, the iterative nature of functions could be optimized for gas efficiency and scalability. |
| Community Governance & Participation | The protocol incorporates mechanisms for community governance, enabling token holders to influence decisions. This fosters a decentralized and participatory ecosystem, aligning with the broader ethos of blockchain development. |
| Error Handling & Input Validation | Functions check for conditions and validate inputs to prevent invalid operations, though the depth of validation (e.g., for edge cases in gameplay or token transactions) would benefit from closer examination. |
i) Other Audit Reports and Automated Findings
Previous Audits There isn't any previous audit (mentioned on C4 overview)
Known issues and risks 4naly3er Report
j) Contract Functionalities
The AI Arena protocol's smart contracts collectively enable a comprehensive gaming ecosystem that integrates NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), competitive AI battles, and a unique economic model. Here's a brief overview of the core functionalities provided by these contracts:
- NFT Management (FighterFarm.sol): Handles the creation, ownership, and attributes of AI-powered NFTs, allowing users to mint, train, and manage their fighters. This contract serves as the foundation for the game's competitive elements, with NFTs representing the virtual fighters in the AI Arena.
High Level UML of FighterFarm.sol
- Gaming Competitions (RankedBattle.sol): Facilitates the AI Arena's competitive gameplay, enabling NFT owners to enter their fighters into ranked battles. It manages match-making, records battle outcomes, updates fighter rankings, and distributes rewards based on performance.
High Level UML of RankedBattle.sol
- Economic System (Neuron.sol, MergingPool.sol): Underpins the protocol's economy through the Neuron (NRN) token and the Merging Pool. NRN tokens are used for various in-game transactions and staking, while the Merging Pool offers a mechanism for players to earn new NFTs by contributing to the pool.
High Level State diagram
-
Staking and Rewards (StakeAtRisk.sol): Allows players to stake NRN tokens on their fighters, influencing their potential rewards from participating in battles. The contract also manages the risks associated with staking, including the possibility of losing staked tokens based on battle outcomes.
-
Voltage Management (VoltageManager.sol): Controls a unique resource called "Voltage," which is required for fighters to participate in battles. It includes functionality for replenishing and spending Voltage, adding another layer of strategy to the game.
k) Full representation of the project’s risk model
Technical Risks
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Bugs or logical errors in the smart contracts can lead to loss of funds, unauthorized access, or unintended behavior. Given the complexity of contracts like the Shrine, interest rate models, and oracle interactions, the attack surface is significant.
Scalability Concerns: As transaction volumes grow, the platform must scale without compromising performance or security.
l) Packages and Dependencies Analysis 📦
| Package | Usage |
|---|---|
openzeppelin | Project uses version 4.7.3 while the recommended version is latest stable version i.e: 5.0.1 |
m) New insights and learning of project from this audit:
Auditing the AI Arena project has provided several key insights and learnings, highlighting the complexity and innovation within blockchain gaming and smart contract development. Here are some notable takeaways from the audit:
-
Complex Ecosystem Interaction: The AI Arena project showcases a multifaceted ecosystem involving NFTs (Fighters), a utility token (NRN), and various gameplay mechanisms (battles, staking, merging pool, etc.). Auditing such a system emphasizes the importance of understanding the interplay between different smart contracts and ensuring that their interactions are secure and perform as intended.
-
Tokenomics and Incentive Structures: The AI Arena's use of NRN tokens and NFTs within its economy highlights the critical role of well-designed tokenomics and incentive structures in driving user engagement and ensuring the long-term viability of blockchain projects. It's fascinating to see how token staking, reward distributions, and the merging pool contribute to an engaging and balanced ecosystem.
-
Technical and Architectural Complexity: The AI Arena project demonstrates a high level of technical and architectural complexity, from managing fighter attributes and battle outcomes to handling token staking and rewards. Auditing such a project provides valuable experience in analyzing and understanding complex smart contract systems, emphasizing the importance of modular design, comprehensive testing, and clear documentation.
-
Innovative Use of Blockchain in Gaming: Lastly, auditing the AI Arena project has been a learning opportunity in seeing the innovative application of blockchain technology in gaming. It showcases the potential for NFTs and cryptocurrencies to revolutionize how games are played, owned, and operated, highlighting a future where players have more control and ownership over their gaming experiences.
In conclusion, auditing the AI Arena project has been a comprehensive learning experience, offering insights into the complexities of developing a blockchain-based gaming ecosystem, the importance of security and governance, and the innovative potential of integrating NFTs and utility tokens into interactive and engaging gameplay.
n) Point of improvements:
The audit of the AI Arena Liquid Infrastructure project has identified several points of improvement that could enhance the project's functionality, security, and user experience. Addressing these areas can contribute significantly to the project's success and sustainability in the rapidly evolving blockchain ecosystem.
1. Upgradeability and Future-proofing
- Implement Upgradeable Smart Contracts: Utilizing proxy contracts or other upgradeability patterns can allow for future improvements and bug fixes without disrupting the existing ecosystem. This approach would enhance the project's flexibility and longevity.
2. Gas Efficiency and Optimization
- Optimize Contract Functions for Gas Usage: Analyzing and optimizing functions, especially those involving loops or large-scale data manipulation, can reduce transaction costs. optimizing storage variables, and minimizing state changes can contribute to efficiency.
4. Security and Auditing
- Expand Bug Bounty Programs: Establishing or expanding bug bounty programs can incentivize the community and security researchers to identify and report vulnerabilities, enhancing the project's overall security posture.
5. Market Adaptation and Integration
- Cross-chain Functionality: Investigating and implementing cross-chain interoperability solutions can open up wider markets and enhance the project's attractiveness by connecting with other blockchain ecosystems.
Conclusion
By addressing these points of improvement, the AI Arena project can not only solidify its foundation but also expand its reach and impact in the DeFi and real-world asset tokenization space. Continuous improvement, driven by community feedback, security practices, and technological advancements, will be key to navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
NOTE: I didn't tracked time when auditing so the timeframe I selected is just a number
Time spent:
3 hours
#0 - c4-pre-sort
2024-02-25T20:21:46Z
raymondfam marked the issue as high quality report
#1 - c4-sponsor
2024-03-04T01:57:02Z
brandinho (sponsor) acknowledged
#2 - c4-judge
2024-03-19T08:25:59Z
HickupHH3 marked the issue as grade-a