DittoETH - roguereggiant's results
A decentralized stablecoin protocol with an order book design for supercharged staking yield.
General Information
Platform: Code4rena
Start Date: 15/03/2024
Pot Size: $60,500 USDC
Total HM: 16
Participants: 43
Period: 21 days
Judge: hansfriese
Total Solo HM: 5
Id: 348
League: ETH
Findings Distribution
Researcher Performance
Rank: 20/43
Findings: 1
Award: $236.67
🌟 Selected for report: 0
🚀 Solo Findings: 0
Findings Information
🌟 Selected for report: popeye
Also found by: 0xbrett8571, JcFichtner, LinKenji, Rhaydden, SAQ, Sathish9098, albahaca, clara, emerald7017, fouzantanveer, foxb868, hunter_w3b, kaveyjoe, roguereggiant
Labels
Awards
236.6726 USDC - $236.67
External Links
Ditto Protocol Overview
This protocol introduces a distinctive approach where bidders and shorters provide ETH, with bidders receiving dUSD while shorters are compensated with the bidders' collateral along with a ShortRecord. This ShortRecord enables shorters to manage their debt position akin to a Collateralized Debt Position (CDP) but with an innovative twist; the collateral and the LST yield go to the shorter, not the asset. This novel structure not only enhances liquidity and financial flexibility but also aligns with Ethereum's decentralization ethos, providing a robust, user-centric financial instrument for the DeFi ecosystem.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BidOrdersFacet.sol | This code defines the BidOrdersFacet contract for creating bid orders within a decentralized finance platform, facilitating market and forced bids with a focus on optimizing gas usage through sorted placements and short matching. It incorporates libraries for mathematical operations, data types, and system-specific logic to manage bids, including updates based on oracle prices and complex bid matching algorithms. |
| ShortOrdersFacet.sol | This code introduces a component focused on creating limit short orders in a market system, emphasizing the exclusive use of limit orders for shorts, with specific parameters for market impact, price, and amount, alongside optimization features for market placement. |
| PrimaryLiquidationFacet.sol | This code outlines a system for executing primary liquidations within a financial market, focusing on enforcing collateral requirements and mitigating undercollateralized positions through forced market bids, alongside managing associated fees and adjustments to ensure market stability and participant incentives. |
| BridgeRouterFacet.sol | This code defines a contract that manages interactions with Ethereum and staked Ethereum bridges, allowing users to deposit and withdraw liquid staking tokens (LST) or Ethereum in exchange for an equivalent value in protocol-specific tokens, aiming to facilitate seamless liquidity movements and yield generation within a decentralized finance ecosystem. |
| ExitShortFacet.sol | This code defines a contract for managing short positions in a trading platform, allowing users to exit their shorts by directly repaying their debt with assets from their wallet or escrowed balance, or by placing a bid in the market to buy back the required amount. It supports partial exits, ensuring users can adjust their positions according to market conditions or their strategy. |
| RedemptionFacet.sol | This contract facilitates the redemption of short positions in a trading platform. It allows users to propose redemptions of undercollateralized short positions, subject to a dispute period, during which other users can challenge the proposed redemptions if they find inaccuracies. Successful redemptions adjust the short positions accordingly, and the redeemer's collateral is updated based on the outcome. |
| LibBridgeRouter.sol | This library manages the interaction between users and different bridges in a decentralized finance platform, handling the credit and debit of digital assets during deposits and withdrawals. It includes functionality to assess bridge credits, calculate withdrawal fees based on market conditions, and adjust user and vault balances accordingly. |
| LibBytes.sol | This library provides functionality to decode and read proposal data for redemption candidates from on-chain storage. It extracts and structures this data into an easily accessible format, focusing specifically on proposals stored using the SSTORE2 contract, which offers optimized storage solutions. |
| LibOracle.sol | This library manages oracle interactions for obtaining and validating asset prices, employing circuit breakers for data reliability and handling deviations in fetched prices. It supports functionality to retrieve prices from both Chainlink oracles and a TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) mechanism, ensuring accurate and secure price data for the protocol. |
| LibOrders.sol | This library orchestrates order management for a decentralized trading platform, providing functions for creating, matching, and canceling limit and market orders, including bids, asks, and shorts. It integrates price verification and updates through oracle checks, manages order queues efficiently using hints for optimized search, and implements complex match-making logic to ensure trades are executed fairly and efficiently within the platform's ecosystem. |
| LibSRUtil.sol | This library provides utility functions for handling operations related to short records within a financial trading system. It manages collateral disbursement, checks for minimum ERC debt requirements, facilitates short record transfers, and updates debt based on changing market conditions, ensuring the integrity and proper functioning of short-related transactions. |
| UniswapOracleLibrary.sol | This library provides functionality to interact with Uniswap V3's pool oracle, offering methods to calculate token exchange amounts based on pool ticks and to estimate time-weighted average prices (TWAP) using the pool's historical data. It aims to facilitate more accurate and decentralized price quotations within smart contracts. |
Architecture System Overview
The system is designed to facilitate market orders, including limit orders for buying and selling assets, creating short orders, liquidating shorts, and handling the redemption of assets in a decentralized finance (DeFi) environment. It heavily relies on smart contracts for managing orders, assets, vaults, and price oracles. Key features include:
- Order Handling: Supports limit and market orders for buying (bids) and selling (asks) assets, including functionality for creating, matching, and canceling orders.
- Short Orders: Allows users to create limit short orders in the market system with functionalities to create, match, and exit shorts.
- Liquidation: Facilitates the liquidation of shorts, allowing users to liquidate shorts under specific conditions.
- Redemption: Enables the submission of short record (SR) candidates for redemption, with a dispute mechanism and collateral claim process.
- Price Oracle Integration: Utilizes external oracles (e.g., Chainlink, Uniswap V3 Oracle) for price data, with mechanisms to handle price discrepancies and ensure accurate pricing information.
- Vault Management: Manages user balances, escrows, and yield distributions within vaults, ensuring the secure storage and handling of assets.
- Bridge Integration: Offers functionality to deposit and withdraw assets through bridge contracts, handling bridge credits and fees to prevent arbitrage.
Architecture Diagram
Overall System Interaction Overview
The system is structured around smart contracts that manage the lifecycle of orders and shorts within a DeFi ecosystem. Users interact with these contracts to perform actions such as creating, matching, or canceling orders, as well as managing shorts through creation, liquidation, and redemption processes. Price data is crucial for many operations, fetched from external oracles like Chainlink or Uniswap V3 to determine accurate market prices for assets.
Vaults play a central role in managing user assets, ensuring secure storage, and handling yield distributions. The bridge integration allows for asset deposits and withdrawals across different blockchains, with mechanisms to manage bridge credits and mitigate arbitrage risks.
Overall, the system facilitates a comprehensive DeFi trading and asset management environment, integrating with external services for price data and cross-chain interactions while maintaining a focus on security and user asset management.
Here's an overall sequence diagram depicting the interaction flow within the system based on the provided Solidity code snippets. The diagram follows a typical flow where a user interacts with the system to place orders, manage shorts, and interact with the vault and oracle systems.
Sequence Diagram
Sequence Diagram Overview
-
Order Handling: Users initiate orders (create, match, cancel) that interact with the order handling contract. This contract may request price data from an oracle and updates the user's balances or order statuses within the vault.
-
Short Orders: Users can create or exit short positions through the Short Orders contract, which also relies on price data from oracles and interacts with the vault for updates.
-
Liquidation: Users can liquidate short positions, necessitating price data and vault interactions to process and confirm the liquidation.
-
Redemption: The redemption process allows users to submit candidates for redemption, potentially disputed, and finally claim redemption, involving price data requests and vault updates.
-
Bridge Integration: Users can deposit or withdraw assets through the Bridge Integration, which communicates with external bridges and updates the vault accordingly.
This sequence diagram provides a high-level overview of the system's interaction flow, highlighting the dependencies on price oracles and vault management for various user-initiated actions.
BidOrdersFacet.sol
Overview of Smart Contract Functions
This smart contract is designed for handling bid orders within a decentralized finance (DeFi) trading platform. It includes functionalities for creating bid orders, matching these orders against asks or shorts, and managing the order flow based on market conditions and oracle price data.
Function: createBid
- Description: Enables users to create bid orders for purchasing ERC tokens at a specified price. Users can choose between market and limit orders and provide hints for gas optimization.
- Parameters:
asset: The market for the bid.price: The price per ERC token in ETH.ercAmount: The amount of ERC tokens to purchase.isMarketOrder: Specifies if the order is a market (true) or limit (false) order.orderHintArray: Array of hint IDs for optimized order placement.shortHintArray: Array of hint IDs for optimized matching with shorts.
- Returns: The amount of ETH filled and the remaining ERC amount not matched.
Function: createForcedBid
- Description: Specifically for exiting shorts, this function allows certain contracts to create a bid order on behalf of a user. It's similar to
createBidbut is only callable by specific contracts. - Parameters:
sender: The address initiating the bid order.asset,price,ercAmount,shortHintArray: Similar tocreateBid.
- Returns: Similar to
createBid, the amounts of ETH filled and ERC left.
Internal Function: _createBid
- Description: Core logic for creating a bid order, used by both
createBidandcreateForcedBid. - Logic Flow:
- Validates the minimum ETH size of the order.
- Escrows the required ETH from the user's vault.
- Determines if the order can be immediately matched with existing asks or shorts.
- Either matches the order, partially or fully, or adds it to the order book.
Function: bidMatchAlgo
- Description: Matches an incoming bid with the lowest available asks or shorts in the order book.
- Parameters:
asset: The market for the bid.incomingBid: The bid order to match.orderHintArray: Optimizes order placement.b: A memory struct containing matching algorithm parameters.
- Returns: The amount of ETH filled and the remaining ERC amount not matched.
Internal Function: matchlowestSell
- Description: Matches the lowest sell order (ask or short) with the incoming bid.
- Parameters: Includes the asset, lowest sell order, incoming bid, and a struct for tracking match totals.
- Logic Flow:
- Calculates the fill amounts for ERC and ETH.
- Adjusts balances and order amounts accordingly.
- Records the match event.
Internal Function: matchIncomingBid
- Description: Finalizes the matching process for an incoming bid, updating the vault balances and order book.
- Parameters: The asset, incoming bid, match totals, and algorithm parameters.
- Returns: The amount of ETH filled and the remaining ERC amount not matched.
Helper Functions
_getLowestSell: Determines the lowest sell order available for matching._shortDirectionHandler: Manages the directional flow of short order matching based on the bid price and oracle data._createBid,bidMatchAlgo, and others interact closely with various libraries (LibAsset,LibOracle,LibOrders,LibShortRecord) for price data, order handling, and vault management.
Overall Functionality
This contract integrates complex DeFi trading mechanisms, such as market and limit bids, short selling, and automatic order matching. It leverages price oracles for accurate market data and implements gas optimization strategies through order hints. The contract is designed to maintain a secure and efficient trading environment, with safeguards like non-reentrancy checks and asset validation.

ShortOrdersFacet.sol
Smart Contract: ShortOrdersFacet
This smart contract facilitates the creation of limit short orders within a trading system, specifically tailored for assets traded on a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform.
Function: createLimitShort
-
Purpose: Allows users to open short positions on a given asset by specifying the price, amount, and initial collateral ratio. This function is designed exclusively for limit shorts.
-
Parameters:
asset: The specific market or asset on which the short is being placed.price: The price at which the user wishes to sell the ERC token, denominated in ETH.ercAmount: The quantity of the ERC token the user wishes to sell short.orderHintArray: An array of order hints used for gas optimization during order placement.shortHintArray: An array of short hints for optimizing matching with shorts above the oracle price.shortOrderCR: The initial Collateral Ratio (CR) for the short order, converted to a uint16 value for the function input.
-
Logic Flow:
- Validates that the market is not frozen and the asset is valid for trading.
- Creates an "empty" short record to initiate the short order process.
- Validates the initial collateral ratio against system-defined thresholds to ensure it's within acceptable bounds.
- Calculates the minimum short amount and the ETH required for the order based on the specified price and ERC amount. It then checks that the order meets the minimum size requirements.
- Confirms the user has sufficient ETH escrowed for collateral based on the initial CR.
- Prepares the short order details, including price, ERC amount, and the initial CR.
- Determines if the order can be matched immediately based on the current highest bid in the order book.
- If the proposed short price is below the oracle price, indicating no immediate match is possible, the order is added to the short order book.
- If the short order's price is above the oracle price, it triggers the sell matching algorithm to attempt to match the short with existing bids.
-
Key Interactions:
- Interacts with various libraries (
LibOrders,LibAsset,LibOracle,LibShortRecord,LibSRUtil) to handle order matching, asset validation, oracle price fetching, short record management, and system rule enforcement. - Uses modifiers to ensure the function is called under proper conditions, such as when the asset is not frozen and is a valid trading pair.
- Emits events to log the creation and potential matching of short orders.
- Interacts with various libraries (
This contract is a critical component of the DeFi platform's trading mechanism, enabling users to speculate on price movements by selling assets short. It integrates with the platform's broader financial and operational rulesets, including collateral management, order matching algorithms, and market conditions monitoring, to facilitate secure and efficient trading activities.

PrimaryLiquidationFacet.sol
Smart Contract: PrimaryLiquidationFacet
This contract enables the liquidation of undercollateralized short positions within a DeFi platform. It is designed to maintain the financial stability of the platform by ensuring all positions are properly collateralized.
Constructor: PrimaryLiquidationFacet
- Purpose: Initializes the contract with a reference to the platform's stablecoin (DUSD).
- Parameters:
_dusd: Address of the platform's stablecoin.
Function: liquidate
- Purpose: Initiates the liquidation process for an undercollateralized short position by forcing the short holder to place a bid in the market. It aims to bring the short position back into a safe collateralization ratio or to eliminate it if recovery is not possible.
- Parameters:
asset: The asset being shorted that is subject to liquidation.shorter: The address of the account holding the short position.id: The identifier of the short position.shortHintArray: An array of hints to optimize the matching process for the forced bid.shortOrderId: The order ID of the short position.
- Returns:
gasFee: The estimated cost of gas incurred by the liquidation process, intended to be partially reimbursed.ethFilled: The amount of ETH filled during the forced bid process.
- Logic Flow:
- Validates the caller and checks for an excessive number of hints.
- Updates the oracle price and checks the short position's collateral ratio.
- Determines the feasibility of liquidation based on the current market conditions and the short position's collateral ratio.
- Executes a forced bid at a slightly higher price to ensure the liquidation can be completed.
- Handles the distribution of fees between the liquidator and the platform.
- Concludes the liquidation by either partially or fully liquidating the short position.
Private Functions:
_checklowestSell: Ensures there are eligible sell orders for liquidation and that prices are within a certain buffer of the oracle price._setLiquidationStruct: Initializes and returns a struct containing all necessary information for the liquidation process._performForcedBid: Executes the forced bid on behalf of the short holder, adjusting collateral and debt as needed._liquidationFeeHandler: Calculates and distributes fees associated with the liquidation._fullorPartialLiquidation: Determines whether the short position can be partially or fully liquidated based on the outcome of the forced bid.
Key Features:
- Maintains the integrity of the DeFi platform by ensuring positions are properly collateralized.
- Utilizes an oracle price to assess the collateralization of short positions.
- Incentivizes external actors to participate in the liquidation process through fee distribution.
- Allows for the socialization of losses in extreme scenarios to protect the platform's stability.
This contract plays a critical role in the risk management framework of the DeFi platform, allowing for the orderly liquidation of positions that fall below required collateralization levels, thereby protecting both the platform and its users from undue financial risk.

BridgeRouterFacet.sol
Smart Contract: BridgeRouterFacet
This contract facilitates interactions between users and bridge protocols, allowing the deposit and withdrawal of assets across different blockchains or layers within a decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
Constructor: BridgeRouterFacet
- Initializes the contract with addresses for two specific bridges: RETH and STETH bridges.
- Parameters:
_rethBridgeand_stethBridgedenote the addresses for RETH and STETH bridge contracts, respectively.
Function: getDethTotal
- Provides the total value of bridged assets (dETH) within a specified vault.
- Parameter:
vaultidentifies the vault for which the total is requested.
Function: getBridges
- Retrieves a list of bridge addresses associated with a given vault.
- Parameter:
vaultspecifies the vault in question.
Function: deposit
- Enables the deposit of LST (Liquidity Staking Tokens) through a specific bridge, in exchange for an equivalent value in dETH (decentralized ETH).
- Parameters include
bridge(the bridge through which the deposit is made), andamount(the quantity of LST being deposited).
Function: depositEth
- Allows for the deposit of ETH via a specified bridge, offering users dETH in return at a 1:1 ratio.
- Parameter:
bridgesignifies the bridge to be used for the ETH deposit.
Function: withdraw
- Facilitates the withdrawal of LST from the protocol via a designated bridge, converting dETH back into the original asset.
- Parameters:
bridge(the bridge through which the withdrawal occurs), anddethAmount(the amount of dETH to be converted and withdrawn).
Function: withdrawTapp
- Permits the withdrawal of assets from the protocol's balance, specifically for use by the DAO.
- Parameters include
bridge(identifying the bridge for withdrawal) anddethAmount(the dETH quantity to be withdrawn).
Private Function: maybeUpdateYield
- Conditionally updates the yield rate for a vault based on the size of the deposit relative to the threshold parameters.
- Parameter:
vaultdenotes the vault being assessed, andamountspecifies the deposit size.
Private Function: _getVault
- Validates the bridge address provided and returns associated vault information.
- Parameter:
bridgespecifies the bridge in question. - Returns:
vault(the vault ID associated with the bridge) andbridgePointer(a numerical representation for the bridge within the vault).
Private Function: _ethConversion
- Calculates the equivalent amount of ETH for a given quantity of dETH, accounting for potential yield or loss within the vault.
- Parameters:
vault(the vault ID) andamount(the dETH quantity). - Returns: The equivalent ETH amount, adjusted for vault performance.
This contract plays a crucial role in bridging assets between different ecosystems, providing liquidity and facilitating cross-chain or layer transactions within the DeFi space. It ensures that assets can move seamlessly across bridges, enhancing interoperability and accessibility for users.

ExitShortFacet.sol
Smart Contract: ExitShortFacet
This contract provides mechanisms for users to exit their short positions in various ways, including using assets from their wallet, assets held in escrow, or by placing bids on the market.
Constructor: ExitShortFacet
- Initializes the contract with the DUSD (decentralized USD) token address.
- _dusd: The address of the DUSD token.
Function: exitShortWallet
- Allows users to exit a short position by burning ERC tokens directly from their wallet.
- asset: The specific market from which to exit the short.
- id: The ID of the short record to exit.
- buybackAmount: The amount of ERC to buy back.
- shortOrderId: The ID of the short order associated with the short record.
Function: exitShortErcEscrowed
- Enables users to exit a short position using ERC tokens that are escrowed in the contract.
- asset: Specifies the market to exit the short from.
- id: Identifies the short record to be exited.
- buybackAmount: Determines the amount of ERC to buy back.
- shortOrderId: The ID of the short order linked to the short record.
Function: exitShort
- Facilitates the exit from a short position by placing a bid on the market.
- asset: The market to exit the short from.
- id: The ID of the short record.
- buybackAmount: The ERC amount to buy back.
- price: The price at which the bid is placed.
- shortHintArray: An array of hint IDs for optimized matching against shorts.
- shortOrderId: The ID of the short order related to the short record.
Private Function: getCollateralRatioNonPrice
- Calculates the collateral ratio of a short record without considering the current price.
- short: The short record for which the collateral ratio is calculated.
- Returns the calculated collateral ratio.
Each function within this contract is designed to offer flexibility in managing short positions, allowing users to close their positions based on their preferred method of settlement, whether that's directly from their wallet, using escrowed assets, or through market transactions. The contract also includes safeguards such as checking for valid short records and ensuring that the operations do not result in adverse conditions like insufficient collateral.

RedemptionFacet.sol
Smart Contract: RedemptionFacet
This contract facilitates the redemption process, allowing users to propose redemptions of short records, challenge proposed redemptions, and claim redeemed collateral.
Helper Function: validRedemptionSR
- Validates a short record for redemption, checking if it is closed, if the ERC debt is above a minimum threshold, and if the proposer is not redeeming their own short record.
Function: proposeRedemption
- Users can propose an array of short records for redemption, subject to a dispute period.
- Parameters include the market asset, a list of proposal inputs (short records), total ERC debt to be redeemed, and the maximum fee the redeemer is willing to pay.
- The function processes each proposed short record, validating it for redemption criteria, and updates the redeemer's escrow balance and the asset's total ERC debt accordingly.
Function: disputeRedemption
- Allows users to challenge a proposed redemption before the dispute period elapses.
- The challenger needs to specify the asset, the redeemer's address, the index of the incorrect proposal, and details of the short record used for the dispute.
- If the dispute is valid, it adjusts the proposed redemption, returning escrowed amounts and adjusting fees as necessary.
Function: claimRedemption
- After the dispute period has elapsed, the redeemer can claim the collateral from the verified redemption candidates.
- This function updates the redeemer's escrow balance to include the redeemed collateral and cleans up the redeemer's proposal data.
Function: claimRemainingCollateral
- Allows shorters to claim any remaining collateral from their short records after redemption has been fully processed and the dispute period has passed.
- Shorters must specify the asset, redeemer's address, their proposal index, and the short record ID to claim their collateral.
Helper Function: _claimRemainingCollateral
- Private function that facilitates the transfer of leftover collateral back to the shorter and closes the short record.
Function: calculateRedemptionFee
- Calculates the redemption fee based on the amount of collateral redeemed and the ERC debt redeemed.
- It updates the asset's base rate and last redemption time to reflect the new state post-redemption.
This contract integrates with several other components, including asset and short record management, to ensure a controlled and fair process for redeeming short positions within the system. It includes mechanisms for proposing redemptions, disputing proposals, and claiming collateral, all while managing fees and ensuring that transactions comply with the platform's rules.

LibBridgeRouter.sol
Smart Contract: LibBridgeRouter
This library facilitates interactions related to bridge transactions within a decentralized finance protocol. It includes functions for adding and withdrawing digital assets through bridge contracts, assessing bridge credits, calculating withdrawal fees based on market conditions, and managing bridge credit transfers.
Function: addDeth
- Credits a user's account with digital ETH (dETH) and updates bridge credit if applicable. It handles scenarios for different vaults, distinguishing between reth and steth bridge credits.
Function: assessDeth
- Determines how much dETH is not covered by bridge credits during a withdrawal operation. It calculates the remaining amount after applying bridge credits and handles different scenarios for withdrawing through reth and steth bridges, including conditions for using credits from one bridge to withdraw from another.
Function: withdrawalFeePct
- Calculates the fee for withdrawing digital assets, intended to prevent free arbitrage. The fee is determined based on the premium/discount differential of the asset relative to its market price. This function is applicable only to a specific vault that contains mixed liquidity tokens (LSTs) like reth and steth.
Function: transferBridgeCredit
- Handles the transfer of bridge credit between users, particularly relevant for non-fungible token (NFT) short records that are being transferred. This function aims to prevent workarounds to the bridge credit system by appropriately adjusting bridge credits during transfers.
Function: removeDeth
- Updates a user's account upon dETH withdrawal. It decreases the user's escrowed ETH and the total dETH balance in the vault by the withdrawn amount, applying any fees associated with the withdrawal.
This library integrates with various parts of the protocol, leveraging bridge contracts to facilitate cross-chain or cross-layer transactions, manage user credits, and ensure proper accounting of digital assets within the ecosystem.

LibBytes.sol
Smart Contract: LibBytes
This library provides functionalities to decode and interpret byte-encoded data specifically tailored for handling proposal data related to redemption operations in a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol.
Function: readProposalData
- Purpose: Decodes byte-encoded proposal data stored using SSTORE2, a library for efficient storage of data on Ethereum. This function is designed to interpret the encoded data into an array of
ProposalDatastructures. - Parameters:
SSTORE2Pointer: The address pointer provided by SSTORE2 where the byte-encoded proposal data is stored.slateLength: The number ofProposalDataentries encoded in the byte array. This is used to initialize the array ofProposalDatastructures to be returned.
- Operation: The function reads the byte array from the specified SSTORE2 address. It then iterates over the array, decoding each entry into a
ProposalDatastructure. This process involves interpreting slices of the byte array as specific data types (e.g.,address,uint8,uint64,uint88) and assigning them to the corresponding fields in aProposalDatastructure. - Decoding Process:
- The function uses assembly for efficient data manipulation and access. It reads 32-byte words from the byte array and shifts/masks bits as necessary to extract the values for
shorter(address),shortId(uint8),CR(uint64),ercDebtRedeemed(uint88), andcolRedeemed(uint88). EachProposalDatastructure requires 51 bytes, and the function calculates offsets accordingly to read the correct segments of the byte array for each field.
- The function uses assembly for efficient data manipulation and access. It reads 32-byte words from the byte array and shifts/masks bits as necessary to extract the values for
- Output: An array of
ProposalDatastructures, each representing a proposal data entry decoded from the byte array.
This library plays a critical role in interpreting stored proposal data for redemption operations, facilitating the retrieval and use of structured information from raw byte-encoded storage.

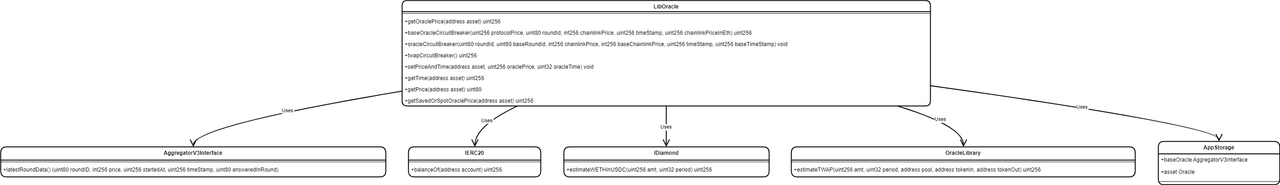
LibOracle.sol
Smart Contract: LibOracle
This library provides functionality related to price oracles, specifically fetching, validating, and managing price data for assets in a decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. It interacts with external oracle services (like Chainlink) and implements mechanisms to ensure the reliability and accuracy of price data.
Function: getOraclePrice
- Purpose: Fetches the latest price for a given asset, performing validation and applying circuit breakers to ensure data integrity.
- Parameters:
asset: The address of the asset for which the price is being fetched.
- Operation: Retrieves the latest price data from the asset's oracle and the base oracle (e.g., for ETH/USD). It checks for invalid or stale data and applies circuit breakers if necessary, including comparing against a Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) as a fallback.
Function: baseOracleCircuitBreaker
- Purpose: Performs validation on price data fetched from the base oracle, applying logic to handle discrepancies, stale or invalid data.
- Parameters:
- Includes protocol price, oracle round ID, Chainlink price, timestamp, and the price converted to ETH.
- Operation: Checks for data validity and compares the oracle price against protocol and TWAP prices to determine the most accurate and up-to-date price.
Function: oracleCircuitBreaker
- Purpose: Validates the price data from an asset-specific oracle against the base oracle to ensure consistency and reliability.
- Parameters:
- Includes round IDs, prices, and timestamps for both the asset-specific and base oracles.
- Operation: Validates the fetched data, ensuring it's not stale or invalid, and ensures that the asset-specific oracle data aligns with the base oracle.
Function: twapCircuitBreaker
- Purpose: Uses a TWAP calculation as a fallback to validate the current price or provide a price estimate when oracle data is unavailable or unreliable.
- Operation: Calculates the TWAP using on-chain liquidity pool data, ensuring there's sufficient liquidity for accurate pricing, and inverts the price to the required format.
Helper Functions for Oracle Data Management
setPriceAndTime: Stores the latest validated price and the timestamp of the update in the contract's storage for a given asset.getTime: Retrieves the timestamp of the last price update for a given asset.getPrice: Fetches the latest stored price for a given asset from the contract's storage.getSavedOrSpotOraclePrice: Returns the stored price if it's recent (less than 15 minutes old) or fetches the current oracle price, validating and applying circuit breakers as necessary.
These functionalities ensure the protocol uses accurate, timely, and reliable price data for its operations, incorporating safeguards against incorrect data and providing mechanisms to handle oracle failures or discrepancies.

LibOrders.sol
Smart Contract: LibOrders
This library provides functionality related to managing orders in a DeFi ecosystem, specifically for a platform that supports trading, shorting, and other order-based operations. It offers mechanisms for creating, canceling, and matching orders, as well as updating oracle prices and managing short records.
Function: getOffsetTime
- Calculates the current time offset from a predefined starting time, providing a relative timestamp used within the contract.
Function: convertCR
- Converts a collateral ratio represented as a
uint16into auint256format, scaling it to match the contract's expected precision.
Order Matching Functions
increaseSharesOnMatch: Updates share counters when an order is matched, used for distributing token rewards.currentOrders: Retrieves a list of current orders for a given asset, providing a snapshot of the market.isShort: Checks if an order is a short order.addBid,addAsk,addShort: Functions for adding bid, ask, and short orders to the respective order books.addSellOrder: Adds an ask or short order to the market, using the appropriate internal function based on the order type.
Function: addOrder
- Adds an order (bid, ask, or short) to the market, linking it within the order book and handling escrow adjustments for the user.
Order Verification and Matching
- Implements a series of functions like
verifyBidId,verifySellId,getOrderId,verifyId,normalizeOrderTypeto validate order placement within the order book, ensuring correct ordering by price and handling order type-specific logic.
Function: cancelOrder, cancelBid, cancelAsk, cancelShort
- Cancels an order by removing it from the order book and adjusting user escrows and short records as necessary. Specific functions handle cancellation for bids, asks, and shorts, accounting for partial fills and ensuring that minimum thresholds are respected.
Oracle and Order Book Management
updateOracleAndStartingShortViaThreshold,updateOracleAndStartingShortViaTimeBidOnly,updateStartingShortIdViaShort: Functions to update the oracle price and the starting short order id based on various triggers like price thresholds or time intervals, ensuring the order book remains in sync with the latest market conditions.findOrderHintId: Finds a hint id for optimized order insertion, aiding in efficient order book updates.
Order Matching and Settlement
sellMatchAlgo: Matches incoming asks against the highest bids, handling partial fills and updating the order book accordingly.matchIncomingSell,matchIncomingAsk,matchIncomingShort: Final settlement functions for matched orders, adjusting user balances and short records.matchHighestBid: Matches the highest bid with an incoming sell order, updating match totals and user balances.
Order Book Updates on Match
updateBidOrdersOnMatch,updateSellOrdersOnMatch,_updateOrders: Update the order book upon order matching, removing filled orders and adjusting links in the bid/ask/short lists.
Utility and Helper Functions
- Includes utility functions like
handlePriceDiscount,min,maxto support order matching logic, price discount adjustments, and basic mathematical operations.
This library centralizes the logic related to order handling, including creating, matching, and canceling orders, as well as integrating oracle price data for accurate market operations. It's crucial for the protocol's trading functionality, ensuring users can trade, short, and manage their orders efficiently within the ecosystem.

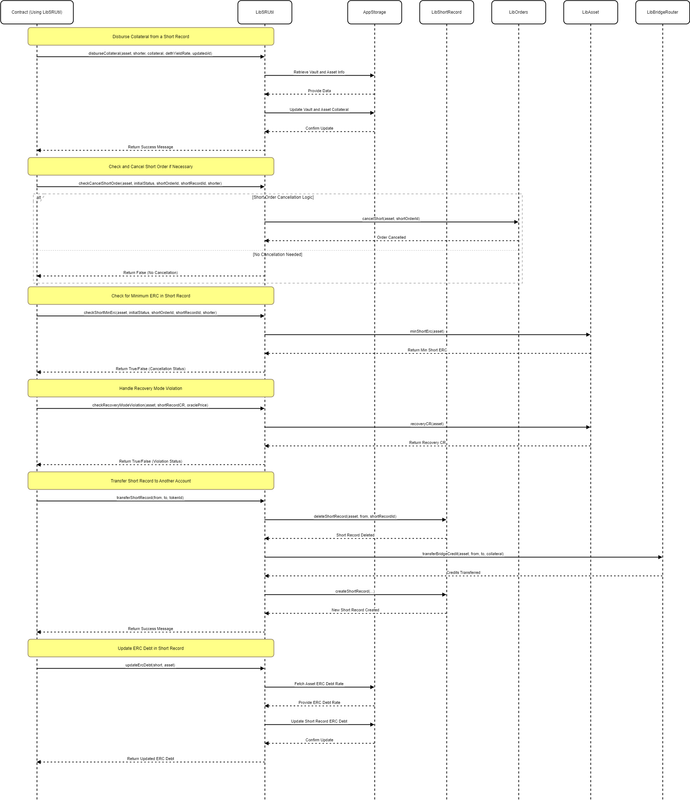
LibSRUtil.sol
Smart Contract: LibSRUtil
This library extends functionalities related to handling short records within a DeFi ecosystem. It offers a range of utilities for managing collateral, validating short orders, and adjusting short positions, particularly in response to market changes or user actions.
Function: disburseCollateral
- Disburses collateral from a short record to the appropriate user, adjusting total collateral figures and distributing any accrued yield.
Function: checkCancelShortOrder
- Validates and potentially cancels a short order based on its fill status and compliance with minimum short requirements.
Function: checkShortMinErc
- Ensures that the remaining short order or record meets the minimum ERC amount required to maintain a valid short position, preventing dust amounts.
Function: checkRecoveryModeViolation
- Assesses whether a short record's collateral ratio violates the protocol's recovery mode conditions, indicating an overly risky position during market stress.
Function: transferShortRecord
- Transfers a short record from one user to another, typically in the case of NFT-backed shorts, handling order cancellation and collateral adjustments as needed.
Function: updateErcDebt
- Updates the ERC debt of a short record based on the latest debt rate from the asset, distributing the debt proportionally among short positions.
These utilities are critical for maintaining the integrity and safety of the platform's shorting mechanism, ensuring that users' positions remain compliant with protocol requirements and that the system can adapt to ongoing changes in market conditions and user strategies.
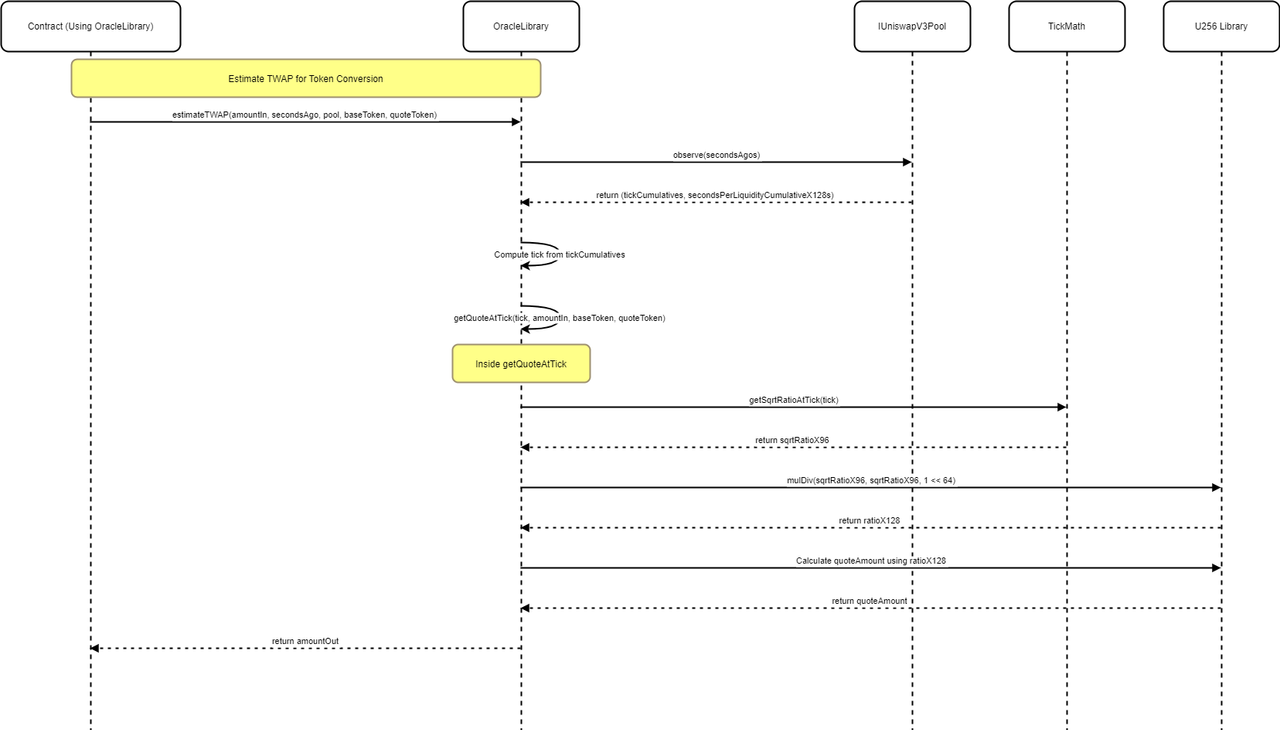
UniswapOracleLibrary.sol
Smart Contract: OracleLibrary
This library offers functionalities to work with the Uniswap V3 pool oracle, enabling the calculation of token exchange amounts based on pool ticks, and estimation of time-weighted average prices (TWAP).
Function: getQuoteAtTick
- Calculates the amount of a quote token received for a given amount of a base token at a specified tick. It supports both directions of trade (base to quote and quote to base) and ensures precision in calculations by adjusting the computation method based on the square root of the price ratio's magnitude.
Function: estimateTWAP
- Estimates the TWAP for converting an amount of a base token to a quote token using Uniswap V3 pool data over a specified period. It retrieves the cumulative tick data for the period, calculates the average tick, and then computes the equivalent quote token amount using the average price implied by the tick. This function ensures accuracy in price estimation over the given timeframe, crucial for applications needing to mitigate against short-term price volatility.
Centralization Risk
Oracle Reliance: The system's dependency on external oracles (e.g., Chainlink, Uniswap V3 Oracles) for asset prices introduces a central point of failure. If these oracles are manipulated or experience downtime, the platform's pricing mechanism could be severely impacted, leading to potential losses for users.
Admin Controls: The presence of administrative functions within the smart contracts, such as those allowing updates to critical system parameters or the ability to pause certain functionalities, could pose a risk if not decentralized or governed by a broad set of stakeholders.
Systematic Risk
Market Volatility: The system's reliance on real-time market data for executing trades, managing collateral ratios, and liquidations exposes users to market volatility risks. Sharp, adverse market movements could lead to systemic failures, especially if compounded by oracle latency or inaccuracies.
Liquidity Constraints: The operations involving bridging assets or settling trades depend on underlying liquidity in external pools (e.g., Uniswap). Insufficient liquidity or large trades relative to the pool size could lead to significant slippage, adversely affecting execution prices.
Architectural Risks
Smart Contract Interdependencies: The system's architecture involves multiple interacting smart contracts (e.g., for handling orders, oracles, asset management). Bugs or vulnerabilities in one contract could potentially compromise the integrity or security of the entire system.
Upgradeability: If the system employs upgradeable contracts, there's a risk of introducing new vulnerabilities during upgrades. Moreover, the process for upgrades needs to be secure and decentralized to prevent malicious changes.
Complexity Risks
Contract Complexity: The multifaceted logic for handling orders, liquidations, and price information introduces significant complexity. Complex systems are more prone to bugs and unintended behaviors, which could be exploited by malicious actors.
Integration Points: The system's integration with external protocols (e.g., Uniswap, Chainlink) adds layers of complexity and potential failure points. Issues in the integrated protocols, such as smart contract vulnerabilities or disruptions in their services, could indirectly affect this system's functionality and security.
User Experience: The complexity of managing multiple types of orders, understanding collateralization ratios, and interacting with various DeFi protocols could pose risks to less experienced users, potentially leading to mistakes that result in financial loss.
This risk assessment highlights areas where the system might be vulnerable due to centralization, market dynamics, architectural decisions, and the inherent complexities of DeFi ecosystems. Mitigating these risks involves thorough testing, audits, clear governance mechanisms, and continuous monitoring of external dependencies.
Conclusion
The system showcases an intricate blend of DeFi functionalities, leveraging smart contracts for asset management, price oracles, and liquidity provision. While it embodies the innovative spirit of decentralized finance, it also inherits risks associated with centralization, market volatility, architectural complexities, and integrations. Mitigation strategies, including rigorous testing, decentralized governance, and user education, are vital for ensuring its robustness and resilience in the dynamic DeFi landscape.
Time spent:
20 hours
#0 - c4-pre-sort
2024-04-07T20:36:26Z
raymondfam marked the issue as high quality report
#1 - c4-judge
2024-04-17T07:14:44Z
hansfriese marked the issue as grade-a